Outer space
Outer space , or just space , is the expanse that exists beyond the Earth and between celestial bodies . Outer space is not completely empty—it is a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , neutrinos , dust , and cosmic rays . The baseline temperature , as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang , is 2.7 kelvins (−270.45 °C; −454.81 °F). [1] The plasma between galaxies accounts for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe; it has a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvins; [2] local concentrations of this plasma have condensed into stars and galaxies . Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, called dark matter , which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces . [3] [4] Observations suggest that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space, which astronomers label dark energy . [5] [6] Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
376260 characters 18 sections 59 paragraphs 33 images 646 internal links 244 external links |
space 0.300 galaxies 0.190 outer 0.178 vacuum 0.169 universe 0.164 intergalactic 0.159 geospace 0.143 medium 0.134 matter 0.129 density 0.121 ebullism 0.119 interstellar 0.118 energy 0.118 blood 0.107 altitude 0.105 |
Outer space , or just space , is the expanse that exists beyond the Earth and between celestial bodies . Outer space is not completely empty—it is a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , neutrinos , dust , and cosmic rays . The baseline temperature , as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang , is 2.7 kelvins (−270.45 °C; −454.81 °F). [1] The plasma between galaxies accounts for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe; it has a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvins; [2] local concentrations of this plasma have condensed into stars and galaxies . Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, called dark matter , which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces . [3] [4] Observations suggest that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space, which astronomers label dark energy . [5] [6] Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. |
|
| 2017 |
362120 characters 18 sections 57 paragraphs 33 images 624 internal links 229 external links |
space 0.303 galaxies 0.192 outer 0.185 vacuum 0.171 universe 0.166 intergalactic 0.161 geospace 0.144 matter 0.130 medium 0.128 density 0.123 ebullism 0.120 energy 0.119 blood 0.108 interstellar 0.107 altitude 0.106 |
Outer space , or just space , is the expanse that exists between celestial bodies , including Earth . Outer space is not completely empty—it is a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , neutrinos , dust , and cosmic rays . The baseline temperature , as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang , is 2.7 kelvins (K) (−270.45 °C; −454.81 °F). [1] The plasma between galaxies accounts for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe; it has a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvins; local concentrations of this plasma have condensed into stars and galaxies . Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, called dark matter , which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces . [2] [3] Observations suggest that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space, which astronomers label dark energy . [4] [5] Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. |
|
| 2016 |
347349 characters 18 sections 57 paragraphs 32 images 616 internal links 183 external links |
space 0.302 vacuum 0.192 geospace 0.181 outer 0.171 intergalactic 0.162 universe 0.161 galaxies 0.159 medium 0.136 matter 0.131 density 0.123 ebullism 0.120 energy 0.115 blood 0.109 interstellar 0.108 cosmic 0.106 |
Outer space , deep space , or just space , is the void that exists between celestial bodies , including Earth . [1] It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , neutrinos , dust and cosmic rays . The baseline temperature , as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang , is 2.7 kelvins (K) (−270.45 °C; −454.81 °F). [2] Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvins in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies . In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter , which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. [3] [4] Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy . [5] [6] Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. |
|
| 2015 |
337798 characters 18 sections 56 paragraphs 31 images 610 internal links 172 external links |
space 0.295 vacuum 0.195 geospace 0.184 outer 0.173 intergalactic 0.164 universe 0.157 medium 0.138 matter 0.133 galaxies 0.127 density 0.125 ebullism 0.122 energy 0.116 blood 0.110 interstellar 0.109 cosmic 0.107 |
Outer space , or just space , is the void that exists between celestial bodies , including the Earth . [1] It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , neutrinos , dust and cosmic rays . The baseline temperature , as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang , is 2.7 kelvins (K) (−270.45 °C; −454.81 °F). [2] Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvins in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies . In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter , which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. [3] [4] Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy . [5] [6] Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. |
|
| 2014 |
316451 characters 18 sections 55 paragraphs 30 images 609 internal links 147 external links |
space 0.303 vacuum 0.192 geospace 0.182 outer 0.171 intergalactic 0.162 universe 0.155 matter 0.138 blood 0.133 medium 0.129 density 0.129 galaxies 0.125 ebullism 0.121 energy 0.115 interstellar 0.108 stars 0.107 |
Outer space , or simply just space , is the void that exists between celestial bodies , including the Earth . [1] It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles: predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium , as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , neutrinos , dust and cosmic rays . The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang , is 2.7 kelvin (K). [2] Plasma with a density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic meter and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies . In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter , which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. [3] [4] Data indicate that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy . [5] [6] Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. |
|
| 2013 |
283674 characters 18 sections 54 paragraphs 23 images 403 internal links 139 external links |
space 0.293 vacuum 0.185 geospace 0.184 outer 0.168 intergalactic 0.164 universe 0.157 matter 0.140 blood 0.135 medium 0.131 density 0.131 galaxies 0.127 ebullism 0.123 energy 0.116 interstellar 0.109 stars 0.109 |
Outer space , or simply space , is the void that exists between celestial bodies , including the Earth . [1] It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles: predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium , as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , neutrinos , dust and cosmic rays . The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang , is 2.7 kelvin (K). [2] Plasma with a density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic meter and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies . In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter , which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. [3] [4] Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy . [5] [6] Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. |
|
| 2012 |
233708 characters 17 sections 47 paragraphs 24 images 322 internal links 102 external links |
space 0.287 geospace 0.205 outer 0.188 vacuum 0.183 intergalactic 0.165 medium 0.137 ebullism 0.136 blood 0.123 density 0.121 stars 0.121 galaxies 0.115 aether 0.115 treaty 0.113 radiation 0.106 universe 0.105 |
Outer space , or simply space , is the void that exists between celestial bodies , including the Earth . [1] It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles: predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium , as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , and neutrinos . Observations and theory suggest that it also contains dark matter and dark energy . The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation left over from the Big Bang , is only 2.7 Kelvin (K); in contrast, temperatures in the coronae of stars can reach over a million Kelvin. Plasma with an extremely low density (less than one hydrogen atom per cubic meter) and high temperature (millions of Kelvin) in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies . Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. |
|
| 2011 |
191440 characters 16 sections 45 paragraphs 12 images 292 internal links 75 external links |
space 0.281 geospace 0.231 vacuum 0.187 intergalactic 0.187 outer 0.186 blood 0.140 ebullism 0.140 density 0.137 universe 0.129 treaty 0.129 medium 0.123 galaxies 0.118 aether 0.118 cosmic 0.105 pressure 0.103 |
Outer space is the void that exists between celestial bodies , including the Earth . [1] It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles: predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium , as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , and neutrinos . Theory suggests that it also contains dark matter and dark energy . In the space between galaxies, matter density can be as low as a few atoms of hydrogen per cubic meter. The baseline temperature, as set by background radiation left over from the Big Bang , is only 3 Kelvin ; in contrast, temperatures in the coronae of stars can reach over a million Kelvin . Plasma with an extremely low density and high temperature, such as warm-hot intergalactic medium and intracluster medium , accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have evolved into stars and galaxies. Intergalactic outer space takes up most of the volume of the universe , but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. As of yet, space travel has been limited to the vicinity of the Solar System ; the remainder of outer space remains inaccessible to humans other than by passive observation with telescopes. |
|
| 2010 |
106497 characters 15 sections 41 paragraphs 9 images 217 internal links 27 external links |
vacuum 0.278 geospace 0.263 space 0.250 intergalactic 0.187 ebullism 0.175 outer 0.150 aether 0.148 blood 0.140 density 0.140 universe 0.117 galaxies 0.115 pressure 0.113 treaty 0.113 medium 0.110 galaxy 0.108 |
Outer space (often simply called space ) is the void that exists beyond any celestial body including the Earth. [1] It is not completely empty (i.e. a perfect vacuum ), but contains a low density of particles, predominantly hydrogen plasma , as well as electromagnetic radiation , magnetic fields , and neutrinos . Theoretically, it also contains dark matter and dark energy . |
|
| 2009 |
108429 characters 15 sections 43 paragraphs 10 images 227 internal links 29 external links |
vacuum 0.278 geospace 0.263 space 0.262 ebullism 0.175 intergalactic 0.164 outer 0.158 aether 0.148 blood 0.140 density 0.132 universe 0.117 galaxies 0.115 pressure 0.113 treaty 0.113 medium 0.110 galaxy 0.108 |
Outer space (often simply called space ) is the space beyond the Earth's atmosphere . [1] Outer space is usually defined from the point of view of the Earth and is used to distinguish it from airspace and terrestrial locations. The term can also be expanded to include the regions outside other celestial bodies in the Solar System (interplanetary space) or the regions outside the Solar System itself (interstellar space). [2] On a universal scale, outer space constitutes the void that exists outside any celestial body . [3] |
|
| 2008 |
66131 characters 10 sections 25 paragraphs 12 images 218 internal links 15 external links |
geospace 0.355 vacuum 0.238 ebullism 0.236 space 0.216 blood 0.189 pressure 0.143 altitude 0.139 lungs 0.133 intergalactic 0.127 atmospheres 0.123 outer 0.122 kármán 0.118 density 0.116 decompression 0.109 boundary 0.106 |
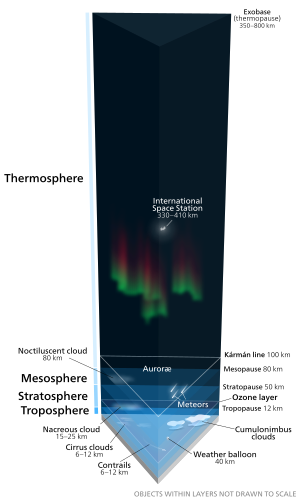
Outer space (often called space ) comprises the relatively empty regions of the universe outside the atmospheres of celestial bodies . Outer space is used to distinguish it from airspace and terrestrial locations. There is no clear boundary between Earth's atmosphere and space as the density of the atmosphere gradually decreases as the altitude increases. Nevertheless, the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale has established the Kármán line at an altitude of 100 kilometres (62 mi)) as a working definition for the boundary between aeronautics and astronautics. This is used because above an altitude of roughly 100 kilometres (62 mi), as Theodore von Kármán calculated, a vehicle would have to travel faster than orbital velocity in order to derive sufficient aerodynamic lift from the atmosphere to support itself. The United States designates people who travel above an altitude of 50 miles (80 km)) as astronauts . During re-entry , roughly 120 kilometres (75 mi) marks the boundary where atmospheric drag becomes noticeable, depending on the ballistic coefficient of the vehicle. |
|
| 2007 |
41525 characters 10 sections 10 paragraphs 6 images 181 internal links 9 external links |
space 0.230 lungs 0.198 vacuum 0.196 velocity 0.184 altitude 0.183 empty 0.162 miles 0.151 bang 0.149 outer 0.141 blood 0.140 centripetal 0.121 orbital 0.119 kármán 0.117 speed 0.115 drag 0.111 |
Outer space , often simply called space , refers to the relatively empty regions of the universe outside the atmospheres of celestial bodies . Outer space is used to distinguish it from airspace (and terrestrial locations). Contrary to popular understanding, outer space is not completely empty (i.e. a perfect vacuum ) but contains a low density of particles, predominantly hydrogen plasma , as well as electromagnetic radiation , dark matter and dark energy . |
|
| 2006 |
29999 characters 9 sections 9 paragraphs 5 images 146 internal links 3 external links |
space 0.214 lungs 0.203 velocity 0.189 altitude 0.188 empty 0.167 vacuum 0.161 miles 0.155 bang 0.153 drag 0.153 outer 0.145 blood 0.144 gradient 0.134 centripetal 0.124 orbital 0.122 gravity 0.119 |
Outer space , also simply called space , refers to the relatively empty regions of the universe outside the atmospheres of celestial bodies. Outer space is used to distinguish it from airspace (and terrestrial locations). Contrary to popular understanding, outer space is not completely empty (i.e. a perfect vacuum ) but contains a low density of particles, predominantly hydrogen gas , as well as electromagnetic radiation . |
|
| 2005 |
22947 characters 4 sections 9 paragraphs 2 images 146 internal links 0 external links |
space 0.221 altitude 0.190 miles 0.179 drag 0.176 outer 0.167 orbital 0.141 speed 0.137 boundary 0.124 orbit 0.121 sea 0.118 bang 0.118 gravity 0.114 floating 0.107 earth 0.102 required 0.097 |
Outer space , also called just space , refers to the relatively empty regions of the Universe outside the atmospheres of celestial bodies. Outer space is used to distinguish it from airspace (and terrestrial locations). Although outer space is certainly spacious , it is far from empty. |
|
| 2004 |
6622 characters 3 sections 7 paragraphs 0 images 26 internal links 0 external links |
altitude 0.331 orbit 0.257 boundary 0.216 miles 0.208 speed 0.190 reaching 0.162 cancels 0.161 craft 0.159 misunderstanding 0.145 karman 0.145 space 0.136 reach 0.134 spaceflight 0.132 thins 0.124 precludes 0.124 |
Outer space (also called just space ), as a name for a region, refers to the relatively empty parts of the Universe , outside the atmospheres of celestial bodies. The term outer space is used to distinguish it from airspace and terrestrial locations. |
|
| 2003 |
874 characters 0 sections 1 paragraphs 0 images 1 internal links 0 external links |
redirect 1.000 |